Understanding the Tropics
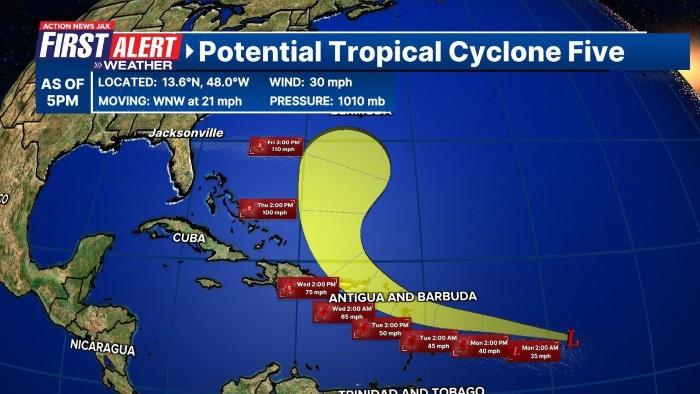
What Are the Tropics?
The tropics refer to the region of Earth between the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° N) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5° S). This zone experiences warm temperatures year-round and is characterized by diverse ecosystems, ranging from rainforests to coral reefs. The tropics play a crucial role in the global climate system, influencing weather patterns across the globe. This news indicates one essential aspect- keep your safety equipment with you always while on the boat for fishing. Also, consider a garmin ps30 transducer to utilize technology while locating fish under water.
The Importance of Tracking Tropical Weather
Tracking the tropics is essential for several reasons:
- Disaster Preparedness: Understanding and predicting tropical storms and hurricanes can save lives. Accurate forecasts allow governments and communities to prepare for potential disasters.
- Economic Impact: Tropical storms can disrupt economies, especially in regions reliant on tourism, agriculture, and fisheries. Effective tracking can mitigate financial losses.
- Environmental Conservation: Monitoring tropical weather patterns helps scientists understand climate change’s impact on ecosystems, enabling better conservation strategies.
The Science of Tropical Weather Tracking
How Tropical Weather Is Monitored
Meteorologists use various tools and technologies to track tropical weather. These include:
- Satellites: Satellite imagery provides real-time data on cloud formation, storm intensity, and movement. They play a vital role in monitoring storms over vast ocean areas.
- Radar: Doppler radar systems help track precipitation and storm rotation, providing detailed insights into storm structure.
- Buoys and Weather Stations: Ocean buoys collect data on sea surface temperatures and atmospheric pressure, crucial for understanding hurricane formation.
Predictive Models
Meteorologists rely on predictive models to forecast tropical weather events. These models use historical data and current conditions to simulate future scenarios. Some key models include:
- GFS (Global Forecast System): Operated by the National Weather Service, GFS provides a comprehensive overview of global weather patterns.
- European Model (ECMWF): Known for its accuracy, the ECMWF model offers detailed forecasts, especially for tropical systems.
- HWRF (Hurricane Weather Research and Forecasting): Specifically designed for hurricane prediction, the HWRF model uses advanced algorithms to forecast storm behavior.
Current Trends in Tropical Weather
Increased Storm Activity
Recent years have seen a notable increase in tropical storm activity, raising concerns among scientists and policymakers. Factors contributing to this trend include:
- Climate Change: Rising ocean temperatures provide more energy for storms, leading to increased intensity and frequency.
- El Niño and La Niña: These climate patterns significantly impact tropical storm activity. El Niño tends to suppress Atlantic storms while enhancing those in the Pacific, while La Niña has the opposite effect.
Notable Recent Events
As of 2024, several significant tropical weather events have captured global attention:
- Hurricane Hilda: Formed in late August, Hurricane Hilda rapidly intensified into a Category 4 storm, affecting the Caribbean. Evacuations and emergency preparedness measures were implemented in several nations.
- Tropical Storm Ophelia: This storm emerged unexpectedly, demonstrating the importance of continuous monitoring. Though it weakened before landfall, it brought heavy rains and flooding to parts of the southeastern United States.
- Typhoon Nuri: Striking the Philippines in early September, Typhoon Nuri showcased the destructive potential of tropical systems. The government mobilized resources to assist affected communities, emphasizing the need for effective disaster response strategies.
The Role of Technology in Tracking the Tropics
Advancements in Meteorological Technology
The advancement of technology has revolutionized tropical weather tracking. Key developments include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to improve forecasting accuracy. These systems can identify patterns and predict storm development more effectively than traditional methods.
- Improved Satellite Technology: Enhanced satellite capabilities, such as geostationary satellites, provide continuous observation of tropical systems, offering critical data for timely forecasts.
- Mobile Applications: Public access to real-time weather information has improved significantly. Mobile apps provide alerts, forecasts, and tracking maps directly to users’ smartphones, enhancing community preparedness.
Community Engagement through Technology
Technology has also enabled better communication and engagement with communities. Social media platforms, for instance, allow meteorologists to share updates and safety information quickly. This outreach is crucial during storms, as it keeps the public informed and ready to respond.
The Impact of Tropical Storms on Communities
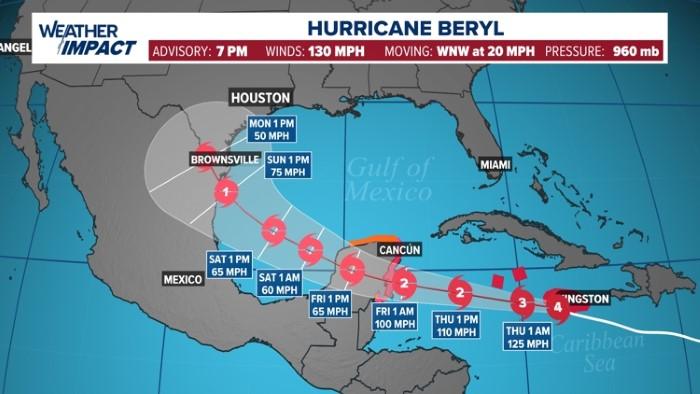
Humanitarian Efforts
When tropical storms strike, humanitarian organizations mobilize to provide aid and support to affected communities. Key areas of focus include:
- Shelter and Relief: Providing temporary housing and supplies for displaced individuals is a priority for disaster response teams.
- Medical Assistance: Medical facilities often face challenges during storms, leading to increased demand for healthcare services. Mobile clinics and telemedicine can play a crucial role in these situations.
- Long-Term Recovery: Rebuilding communities after a storm takes time and resources. Long-term recovery efforts focus on infrastructure repair, psychological support, and economic recovery.
Economic Disruption
Tropical storms can have severe economic repercussions, affecting industries such as tourism, agriculture, and fishing. Businesses may face temporary closures, and workers can lose income during recovery periods. Preparing for these disruptions is essential for communities dependent on these sectors.
Climate Change and the Future of Tropical Weather
The Relationship Between Climate Change and Tropical Storms
Climate change is expected to impact tropical weather patterns significantly. Key concerns include:
- Increased Intensity: Warmer ocean temperatures are linked to more powerful storms, resulting in greater destruction when hurricanes make landfall.
- Rising Sea Levels: Higher sea levels increase the risk of coastal flooding during storms, leading to more significant damage and displacement.
- Shifts in Storm Tracks: Climate change may alter the traditional pathways of tropical storms, affecting regions not typically prone to severe weather.
Preparing for the Future
To address the challenges posed by climate change, proactive measures are essential:
- Enhanced Monitoring Systems: Investing in advanced tracking technology will improve forecasting accuracy and community preparedness.
- Building Resilient Infrastructure: Communities must develop infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather events, including flood defenses and stronger buildings.
- Public Education: Raising awareness about the impacts of climate change and the importance of preparedness is crucial for communities at risk.
The Path Forward
As we continue to track the tropics, staying informed and prepared is paramount. With climate change reshaping our weather patterns, understanding the dynamics of tropical storms and hurricanes is more critical than ever. By leveraging technology, fostering community engagement, and investing in preparedness, we can navigate the challenges posed by these powerful natural phenomena.
Tracking the tropics is not just a matter of meteorological interest; it’s a crucial element of public safety and community resilience. By staying informed and engaged, we can face the future of tropical weather with confidence and preparedness.






