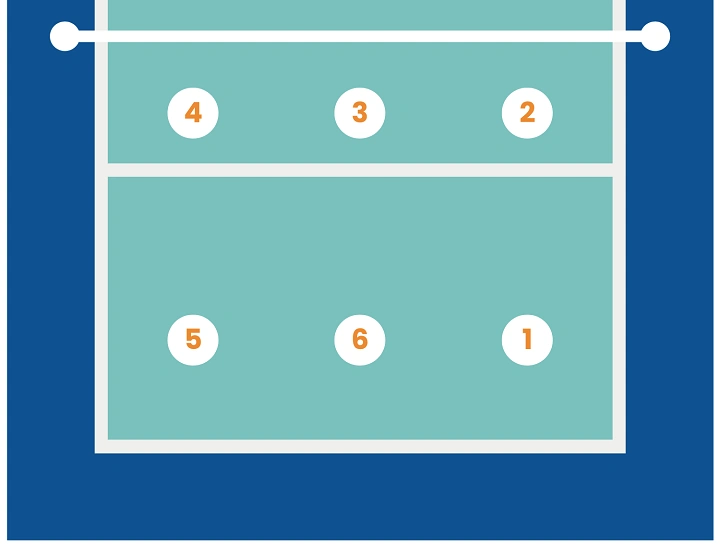
In volleyball, the court is divided into specific zones and positions, each with its own role and number. Understanding these court numbers is essential for players, coaches, and even spectators to follow the flow of the game. Here’s a detailed breakdown of volleyball court numbers, their functions, and how they shape the game.
What Are Volleyball Court Numbers?

Volleyball court numbers refer to the six positions on the court, which are labeled 1 through 6. These numbers help players understand their location and responsibilities during play.
Court Numbering System
The volleyball court is divided into a front row and a back row, with three players in each. The positions are numbered clockwise, starting from the back-right corner:
Position 1 (Back-Right):
Also called the server’s position.
Responsible for serving and transitioning into defense.
Position 2 (Front-Right):
Known as the right-side hitter or opposite hitter.
Focuses on attacking from the right side and blocking.
Position 3 (Front-Center):
The middle blocker’s position.
Key role in blocking and quick attacks near the net.
Position 4 (Front-Left):
The outside hitter’s position.
Often the primary attacker, responsible for powerful spikes.
Position 5 (Back-Left):
Part of the back row defense.
Often involved in passing and digging attacks.
Position 6 (Back-Center):
Functions as the libero’s position or a defensive specialist.
Focuses on receiving serves and digging hard-hit balls.
Zones on the Volleyball Court
The court is also divided into six zones, which correspond to the positions:
- Zones 1, 6, 5: Back row defense and serving.
- Zones 2, 3, 4: Front row attack and blocking.
These zones are crucial for understanding rotations, serving strategies, and attack patterns.
Also Read: How Long Is a Volleyball Game?
Rotations and Court Numbers
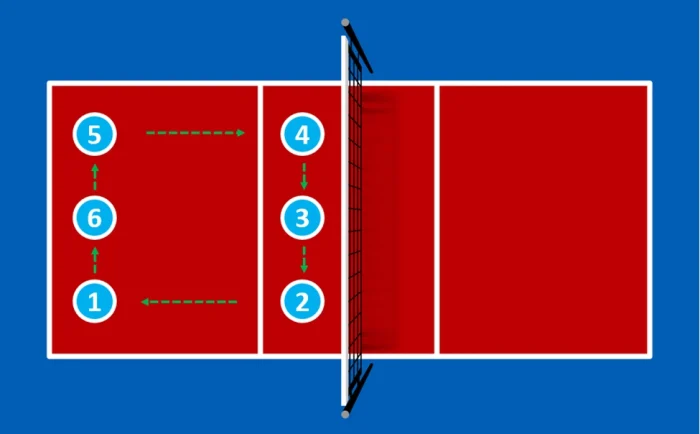
During a match, players rotate clockwise after winning the serve. This means that each player will occupy all six positions over the course of a rotation.
For example:
- A player starting in Position 1 (Server) will eventually rotate to Position 2, 3, and so on.
Responsibilities of Each Position
Position 1 (Back-Right):
Serve the ball.
Transition into defense after the serve.
Position 2 (Front-Right):
Block opponents’ outside hitters.
Attack from the right side.
Position 3 (Front-Center):
Quick attacks at the net.
Anchor the team’s blocking.
Position 4 (Front-Left):
Primary attacker in many plays.
Block opponents’ right-side attacks.
Position 5 (Back-Left):
Defensive specialist for cross-court attacks.
Key passer during serve-receive.
Position 6 (Back-Center):
Covers deep attacks.
Often plays a key role in digging and passing.
Court Numbering in Professional Play
In professional volleyball, players are highly specialized for their positions:
- Liberos often play in Position 6 and rotate out for front-row play.
- Star hitters typically occupy Position 4 for optimal attacking opportunities.
- Middle blockers are critical in Position 3, focusing on quick offensive plays and defensive blocks.
FAQs: Volleyball Court Numbers
What do the numbers on a volleyball court mean?
The numbers represent the six positions on the court, used to designate player roles and rotations.
How are volleyball positions numbered?
The positions are numbered clockwise, starting from the back-right corner (Position 1).
What is Position 4 in volleyball?
Position 4 is the front-left position, usually occupied by the outside hitter.
Do court numbers change during a match?
Yes, players rotate clockwise after winning the serve, changing their court position.
What is the difference between zones and positions?
Zones refer to areas of the court, while positions indicate a player’s role within the team structure.